| Welcome to Sprocket School! This project is maintained by volunteer editors. Learn more about how this works. |
16mm sound formats: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with "* mono - various types (mauer, single track, etc) (stereo was developed in the 1990s and some Eastman projectors have readers for this but no prints were made) * silent (double perf vs. single perf) * sound from external sources (digital file, cassette tape, radio, etc.) * mag stripe (rare for standard projection settings but comes up with home movies and artifacts like Scopitones) * production elements you may run into (e.g. fullcoat) * DTS exists in very rare, semi-exp..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=Gallery= | =Gallery= | ||
<gallery widths=200px heights=200px> | |||
File:Mauer track.JPG|An example of a ''Mauer track''.]] | |||
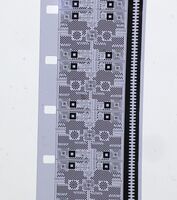
File:16mm test film.jpg | |||
File:16mm-mono-single.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
[Category:16mm] | [[Category:16mm]] | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 15 October 2025
- mono - various types (mauer, single track, etc) (stereo was developed in the 1990s and some Eastman projectors have readers for this but no prints were made)
- silent (double perf vs. single perf)
- sound from external sources (digital file, cassette tape, radio, etc.)
- mag stripe (rare for standard projection settings but comes up with home movies and artifacts like Scopitones)
- production elements you may run into (e.g. fullcoat)
- DTS exists in very rare, semi-experimental cases, but this is not something you will run into in an ordinary projection setting.
Gallery
-
An example of a Mauer track.]]
![An example of a Mauer track.]]](/w/images/thumb/1/13/Mauer_track.JPG/200px-Mauer_track.JPG)